Acupuncture treat
Poststroke Syndrome
中醫針灸治療
中風後遺症
Acupuncture treat
Poststroke Syndrome
中醫針灸治療中風後遺症
Underlying points are on Vagus nerve.
夾 T - L spine level at :
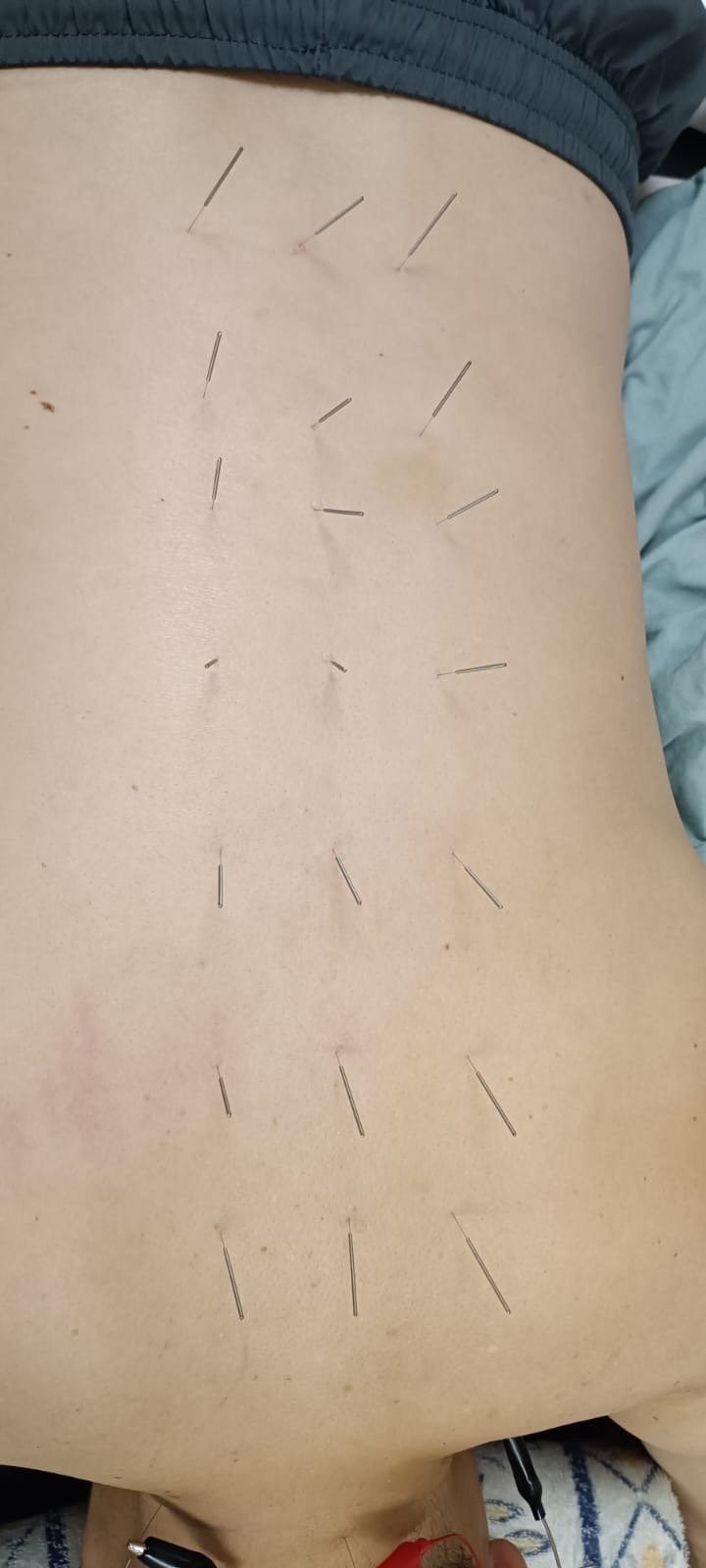
T3, T5, T7, T9, T11, L1, L2. = 肺, 心, 膈, 肝, 脾, 三焦, 腎. 用卡啦夾針法, 即1and4, 2and 5, 3and 6....增加針距離.用30 mm 針.
手手三針: 左右 合谷, 外關, 曲池. A5B1, A3B3, A2B1, A1B1. 各三分鐘.
Treat Poststroke Syndrome with Hua Tuo Jiaji Points Acupuncture
The underlying acupuncture points target the vagus nerve.
Jiaji Points at T-L Spine Levels:
T3, T5, T7, T9, T11, L1, L2
Corresponding organs: Lungs, Heart, Diaphragm, Liver, Spleen, Sanjiao, Kidneys
Technique: Use the "Kala Paired Needling" method:
Pair 1 & 4, 2 & 5, 3 & 6, increasing the spacing between needles.
Use 30mm needles.
Hand Acupuncture (Three Needles on Each Hand):
Points: Hegu (LI4), Waiguan (SJ5), Quchi (LI11) (bilateral).
Frequencies: A5B1, A3B3, A2B1, A1B1
Duration: 3 minutes per setting
Vitamin B1 Therapy treat
Poststroke Syndrome
Acupuncture treat
Facial Paralysis
中醫針灸治療面癱
Q 請問你,如果面癱在2022,出現後遺症至今2年,主症左眼眼皮眨眼開關遲頓(中度差),以你經驗,仲有無得再攪,再改善呢?請指教.
Q I would like to ask you, if you suffer from facial paralysis in 2022 and have had sequelae for 2 years now, the main symptom is delayed blinking and closing of the left eyelid (moderately poor), based on your experience, is it possible to further trouble and improve it?
A Yes有. This is happen is because of 現在的情況是 Scar impingement on facial(7th) nerve of facial expressions. Can retrieve 70-85% by this method. Needles are at nerve outlets starting from TMJ (TemporoMandibular Joint.牙關節.) outlet. + 翳風,聽宮,下關, 風池..穴位. 5/1, 3/3,2/1,1/1.
Use needles. Very much more effective than probes. Use probes each pair will take 4-5 minutes.
MCT5.3 microcurrent device
5/1 3min
3/3 3min
2/1 3min
1/1 3min
針灸治療面癱
穴位位置
翳風 SJ17, 在耳後陷者中
聽宮 SI19,耳屏(耳珠)中央前,張口時呈凹陷處
下關 ST7, 面部耳前方,顴弓與下頜切跡所形成的凹陷中。張口肘下頜骨髁狀突前移,凹陷即消失
風池 GB20,
地倉ST4, 當口角旁4分,目中線上
禾髎LI19, 「口禾髎」,上唇部,鼻孔外緣直下, 當水溝 旁5分,上頜骨尖牙窩部
口歪:禾髎、地倉
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and the largest nerve in the face. It is a mixed nerve containing both sensory and motor fibers. It has three major branches:
Ophthalmic Nerve (V1) – Responsible for sensation in the eyes, forehead, and nose.
Maxillary Nerve (V2) – Provides sensation to the upper jaw, teeth, nasal cavity, and upper lip.
Mandibular Nerve (V3) – Supplies sensation to the lower jaw, teeth, lower lip, and tongue, and also controls the muscles involved in chewing.
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve and is also a mixed nerve, containing motor, sensory, and parasympathetic fibers. Its main functions include:
Motor Function – Controls facial expression muscles, such as those used for smiling, frowning, and closing the eyes.
Sensory Function – Responsible for taste sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
Parasympathetic Function – Regulates the secretion of the salivary and lacrimal glands.